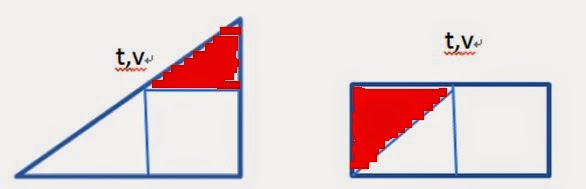
從反面去想會比較簡單:全部扣掉不用扣的,即為需要移動的步數。
字典順序:
可以把他想成每次都從最小的開始排起
ex: 1 2 3 4 下一個是 1 2 4 3、1 4 2 3 ....
ex: BCD 下一個是 BDC、CBD
我的寫法並不是很好, 全部一個一個列出來~
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int color[3][3]={0};
int i,j;
char buf[4]={0};
int total,minMove,temp;
/*BGC*/
while(scanf("%d %d %d",&color[0][0],&color[0][1],&color[0][2])!=EOF){
total = color[0][0] + color[0][1] + color[0][2];
for(i=1;i<3;++i){
for(j=0;j<3;++j){
scanf("%d",&color[i][j]);
total += color[i][j];
}
}
minMove=total;
/*BCG*/
temp = total - color[0][0] - color[1][2] - color[2][1];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"BCG");
}
/*BGC*/
temp = total - color[0][0] - color[1][1] - color[2][2];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"BGC");
}
/*CBG*/
temp = total - color[0][2] - color[1][0] - color[2][1];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"CBG");
}
/*CGB*/
temp = total - color[0][2] - color[1][1] - color[2][0];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"CGB");
}
/*GBC*/
temp = total - color[0][1] - color[1][0] - color[2][2];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"GBC");
}
/*GCB*/
temp = total - color[0][1] - color[1][2] - color[2][0];
if(temp < minMove){
minMove = temp;
strcpy(buf,"GCB");
}
printf("%s %d\n",buf,minMove);
}
return 0;
}
2014年6月30日 星期一
uva 458 The Decoder
從範例測資可以知道原本的字元和轉換過的字元相差 7
1JKJ'pz'{ol'{yhklthyr'vm'{ol'Jvu{yvs'Kh{h'Jvywvyh{pvu5
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void){
char buf[100000]={0};
int i;
while(fgets(buf,10000-1,stdin)){
for(i=0;i<strlen(buf)-1;i++){
buf[i]-=7;
}
buf[i]='\0';
puts(buf);
}
return 0;
}
1JKJ'pz'{ol'{yhklthyr'vm'{ol'Jvu{yvs'Kh{h'Jvywvyh{pvu5
減 7 =>*CDC is the trademark of the Control Data Corporation.
怕測資有空白,可以採用 fgets 讀取,fgets 讀到檔尾的時候,return NULL。
使用 puts 印出內容時,最後一個字元為 '\n',所以要先把最後一個字元換成 '\0'
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void){
char buf[100000]={0};
int i;
while(fgets(buf,10000-1,stdin)){
for(i=0;i<strlen(buf)-1;i++){
buf[i]-=7;
}
buf[i]='\0';
puts(buf);
}
return 0;
}
uva 10071 - Back to High School Physics
particle 是等加速度在運動:
位移 = 速度 * 時間 * 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int v,t;
while( scanf("%d %d",&v,&t) != EOF)
printf("%d\n", 2*t*v);
return 0;
}
位移 = 速度 * 時間 * 2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int v,t;
while( scanf("%d %d",&v,&t) != EOF)
printf("%d\n", 2*t*v);
return 0;
}
uva 10055 - Hashmat the Brave Warrior
The input numbers are not
greater than 2^32
題目中,input 的這句話表示 int 不能處理,須使用更大的型別。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void){
double num1, num2;
while(scanf("%lf %lf",&num1,&num2)!=EOF)
printf("%.0lf\n", fabs(num1-num2) );
return 0;
}
題目中,input 的這句話表示 int 不能處理,須使用更大的型別。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void){
double num1, num2;
while(scanf("%lf %lf",&num1,&num2)!=EOF)
printf("%.0lf\n", fabs(num1-num2) );
return 0;
}
2014年6月25日 星期三
uva 141 The Spot Game
思考這題的時候,不用怕因為要一直往前 check 而導致 TLE,測資的大小可以以這種方式在時間內跑完。
所以直接把過程 code 即可。
我有做一個黑點 counter 的比較,如果 counter 不同,就一定不同,不用再掃四個二維陣列。
function 的部分只要掃轉移個方向的,其他三個情形直接呼叫同一個 function 來轉。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct grid{
int g1[51][51];
int g2[51][51];
int g3[51][51];
int g4[51][51];
int counter;
};
struct grid boxs[100];
void r90(int a[51][51], int b[51][51], int N){
int i,j,m,n;
for(i=N,n=1;i>=1;--i,++n){
for(j=1,m=1;j<=N;++j,++m){
b[m][n]=a[i][j];
}
}
return;
}
int check(struct grid a,int b[51][51],int N,int bcounter){
int i,j,ok;
if(a.counter!=bcounter)
return 1;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g1[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g2[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g3[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g4[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int main(void){
int N, top, i,j;
int x,y;
char c;
int pass;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&N);
if(N==0) break;
for(i=1,top=-1,pass=0;i<=2*N;++i){
scanf("%d %d %c",&x,&y,&c);
if(pass==1) continue;
if(top==-1){
boxs[++top].counter=1;
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=1;
r90(boxs[top].g1,boxs[top].g2, N);
r90(boxs[top].g2,boxs[top].g3, N);
r90(boxs[top].g3,boxs[top].g4, N);
}else{
++top;
boxs[top]=boxs[top-1];
if(c=='+'){
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=1;
++boxs[top].counter;
}else{
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=0;
--boxs[top].counter;
}
for(j=0;j<top;++j){
if( check(boxs[j],boxs[top].g1,N,boxs[top].counter) ==0 ){
if(i%2==0){
printf("Player 1 wins on move %d\n",i);
}else{
printf("Player 2 wins on move %d\n",i);
}
pass=1;
break;
}
}
r90(boxs[top].g1,boxs[top].g2, N);
r90(boxs[top].g2,boxs[top].g3, N);
r90(boxs[top].g3,boxs[top].g4, N);
}
}
if(i>2*N && pass!=1)
printf("Draw\n");
}
return 0;
}
所以直接把過程 code 即可。
我有做一個黑點 counter 的比較,如果 counter 不同,就一定不同,不用再掃四個二維陣列。
function 的部分只要掃轉移個方向的,其他三個情形直接呼叫同一個 function 來轉。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct grid{
int g1[51][51];
int g2[51][51];
int g3[51][51];
int g4[51][51];
int counter;
};
struct grid boxs[100];
void r90(int a[51][51], int b[51][51], int N){
int i,j,m,n;
for(i=N,n=1;i>=1;--i,++n){
for(j=1,m=1;j<=N;++j,++m){
b[m][n]=a[i][j];
}
}
return;
}
int check(struct grid a,int b[51][51],int N,int bcounter){
int i,j,ok;
if(a.counter!=bcounter)
return 1;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g1[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g2[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g3[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
ok=0;
for(i=1;i<=N;++i){
for(j=1;j<=N;++j){
if(a.g4[i][j]!=b[i][j]){
ok=1;
}
}
}
if(ok==0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
int main(void){
int N, top, i,j;
int x,y;
char c;
int pass;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&N);
if(N==0) break;
for(i=1,top=-1,pass=0;i<=2*N;++i){
scanf("%d %d %c",&x,&y,&c);
if(pass==1) continue;
if(top==-1){
boxs[++top].counter=1;
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=1;
r90(boxs[top].g1,boxs[top].g2, N);
r90(boxs[top].g2,boxs[top].g3, N);
r90(boxs[top].g3,boxs[top].g4, N);
}else{
++top;
boxs[top]=boxs[top-1];
if(c=='+'){
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=1;
++boxs[top].counter;
}else{
boxs[top].g1[x][y]=0;
--boxs[top].counter;
}
for(j=0;j<top;++j){
if( check(boxs[j],boxs[top].g1,N,boxs[top].counter) ==0 ){
if(i%2==0){
printf("Player 1 wins on move %d\n",i);
}else{
printf("Player 2 wins on move %d\n",i);
}
pass=1;
break;
}
}
r90(boxs[top].g1,boxs[top].g2, N);
r90(boxs[top].g2,boxs[top].g3, N);
r90(boxs[top].g3,boxs[top].g4, N);
}
}
if(i>2*N && pass!=1)
printf("Draw\n");
}
return 0;
}
2014年6月24日 星期二
uva 105 The Skyline Problem
把比較高的覆蓋比較低的。
注意:
用兩個點形成線段,所以在寫程式時,要保持這個觀點去寫。
ex: y[i] 存的高度為 i-1 和 i 形成的線段高度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int y[12000]={0};
int l,h,r,maxx;
int i,temp;
maxx=0;
while(scanf("%d %d %d",&l,&h,&r)!=EOF){
for(i=l+1;i<=r;i++){
if(h>y[i])
y[i]=h;
if(r>maxx)maxx=r;
}
}
i=0;
while(y[i]==0)++i;
printf("%d %d",i-1,y[i]);
for(;i<=maxx;++i){
if(y[i]!=y[i+1])
printf(" %d %d",i,y[i+1]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
注意:
用兩個點形成線段,所以在寫程式時,要保持這個觀點去寫。
ex: y[i] 存的高度為 i-1 和 i 形成的線段高度
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int y[12000]={0};
int l,h,r,maxx;
int i,temp;
maxx=0;
while(scanf("%d %d %d",&l,&h,&r)!=EOF){
for(i=l+1;i<=r;i++){
if(h>y[i])
y[i]=h;
if(r>maxx)maxx=r;
}
}
i=0;
while(y[i]==0)++i;
printf("%d %d",i-1,y[i]);
for(;i<=maxx;++i){
if(y[i]!=y[i+1])
printf(" %d %d",i,y[i+1]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
uva 11039 Building designing
用 Greedy 的方法:
最開始,挑兩種顏色中,最小的先擺下面,再來輪流放該顏色最小可以放得上去。
堆完之後,即為最大高度。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int compare(const void *a, const void* b){
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main(void){
int amount, floor;
int i,j, neg,pos, temp;
int counter;
int *nn, *pp;
nn = malloc(sizeof(int)*500000);
pp = malloc(sizeof(int)*500000);
scanf("%d",&amount);
while(amount--){
scanf("%d",&floor);
for(i=0,neg=-1,pos=-1;i<floor;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(temp<0){
nn[++neg]=temp*(-1);
}else{
pp[++pos]=temp;
}
}
qsort(nn,neg+1,sizeof(int),compare);
qsort(pp,pos+1,sizeof(int),compare);
i=j=counter=0;
if(neg>=0&&pos>=0){
if(pp[i]>nn[j]){
temp= (-1) * nn[j];
++j;
}else{
temp=pp[i];
++i;
}
++counter;
}else if(neg>=0 || pos>=0){
counter=1;
}
while(j<=neg&&i<=pos&&temp!=0){
if(temp>=0){
while(j<=neg){
if(nn[j] > temp){
++counter;
temp=nn[j]*(-1);
++j;
break;
}
++j;
}
}else{
while(i<=pos){
if(pp[i] > temp*(-1)){
++counter;
temp=pp[i];
++i;
break;
}
++i;
}
}
}
if(counter>1){
if(temp>=0){
while(j<=neg){
if(nn[j] > temp){
++counter;
++j;
break;
}
++j;
}
}else{
while(i<=pos){
if(pp[i] > temp*(-1)){
++counter;
++i;
break;
}
++i;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",counter);
}
return 0;
}
最開始,挑兩種顏色中,最小的先擺下面,再來輪流放該顏色最小可以放得上去。
堆完之後,即為最大高度。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int compare(const void *a, const void* b){
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int main(void){
int amount, floor;
int i,j, neg,pos, temp;
int counter;
int *nn, *pp;
nn = malloc(sizeof(int)*500000);
pp = malloc(sizeof(int)*500000);
scanf("%d",&amount);
while(amount--){
scanf("%d",&floor);
for(i=0,neg=-1,pos=-1;i<floor;i++){
scanf("%d",&temp);
if(temp<0){
nn[++neg]=temp*(-1);
}else{
pp[++pos]=temp;
}
}
qsort(nn,neg+1,sizeof(int),compare);
qsort(pp,pos+1,sizeof(int),compare);
i=j=counter=0;
if(neg>=0&&pos>=0){
if(pp[i]>nn[j]){
temp= (-1) * nn[j];
++j;
}else{
temp=pp[i];
++i;
}
++counter;
}else if(neg>=0 || pos>=0){
counter=1;
}
while(j<=neg&&i<=pos&&temp!=0){
if(temp>=0){
while(j<=neg){
if(nn[j] > temp){
++counter;
temp=nn[j]*(-1);
++j;
break;
}
++j;
}
}else{
while(i<=pos){
if(pp[i] > temp*(-1)){
++counter;
temp=pp[i];
++i;
break;
}
++i;
}
}
}
if(counter>1){
if(temp>=0){
while(j<=neg){
if(nn[j] > temp){
++counter;
++j;
break;
}
++j;
}
}else{
while(i<=pos){
if(pp[i] > temp*(-1)){
++counter;
++i;
break;
}
++i;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",counter);
}
return 0;
}
uva 10783 Odd Sum
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
int amount, low, high;
int sum,i;
scanf("%d",&amount);
i=1;
while(i<=amount){
scanf("%d",&low); scanf("%d",&high);
for(sum=0;low<=high;low++){
if(low%2!=0){
sum+=low;
}
}
printf("Case %d: %d\n",i,sum);
++i;
}
return 0;
}
uva 101 The Blocks Problem
follow 題目的規定操作即可。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void){
int amount,num1, num2;;
char c1[10] = {0}, c2[10] = {0};
int table[25]={0},a[25][25],top[25], prepare[25];
int target, order, pre_top;
int i,j, temp;
char c;
while(scanf("%d", &amount)!=EOF){
for(i=0;i<amount;i++){
a[i][0]=i;
table[i]=i;
top[i]=0;
}
while(1){
scanf("%s", &c1);
if(strcmp(c1,"quit")==0)
break;
scanf(" %d %s %d%c",&num1,&c2,&num2,&c);
if( (num1==num2) || (table[num1]==table[num2]) )
continue;
if(strcmp(c1,"move")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num1]] ; a[ table[num1] ][ temp ] != num1 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num1] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num1] ] = temp-1;
if(strcmp(c2,"onto")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num2]] ; a[ table[num2] ][ temp ] != num2 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num2] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num2] ] = temp + 1;
order = top[ table[num2] ];
a[ table[num2] ][order] = num1;
}else if(strcmp(c2,"over")==0){
++top[ table[num2] ];
order = top[ table[num2] ];
a[ table[num2] ][order] = num1;
}
table[num1]=table[num2];
}else if(strcmp(c1,"pile")==0){
for(i=0; a[ table[num1] ][i] != num1 ;i++);
temp = i-1;
for(pre_top=-1;i<=top[ table[num1] ];i++)
prepare[++pre_top]=a[ table[num1] ][i];
top[ table[num1] ] = temp;
if(strcmp(c2,"onto")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num2]] ; a[ table[num2] ][ temp ] != num2 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num2] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num2] ] = temp;
}
for(order=top[ table[num2] ], i=0 ; i<=pre_top ; i++){
a[table[num2]][++order] = prepare[i];
table[prepare[i]] = table[num2];
}
top[table[num2]] = order;
}
}
for(i=0;i<amount;i++){
printf("%d:",i);
for(j=0;j<=top[i];j++)
printf(" %d",a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void){
int amount,num1, num2;;
char c1[10] = {0}, c2[10] = {0};
int table[25]={0},a[25][25],top[25], prepare[25];
int target, order, pre_top;
int i,j, temp;
char c;
while(scanf("%d", &amount)!=EOF){
for(i=0;i<amount;i++){
a[i][0]=i;
table[i]=i;
top[i]=0;
}
while(1){
scanf("%s", &c1);
if(strcmp(c1,"quit")==0)
break;
scanf(" %d %s %d%c",&num1,&c2,&num2,&c);
if( (num1==num2) || (table[num1]==table[num2]) )
continue;
if(strcmp(c1,"move")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num1]] ; a[ table[num1] ][ temp ] != num1 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num1] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num1] ] = temp-1;
if(strcmp(c2,"onto")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num2]] ; a[ table[num2] ][ temp ] != num2 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num2] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num2] ] = temp + 1;
order = top[ table[num2] ];
a[ table[num2] ][order] = num1;
}else if(strcmp(c2,"over")==0){
++top[ table[num2] ];
order = top[ table[num2] ];
a[ table[num2] ][order] = num1;
}
table[num1]=table[num2];
}else if(strcmp(c1,"pile")==0){
for(i=0; a[ table[num1] ][i] != num1 ;i++);
temp = i-1;
for(pre_top=-1;i<=top[ table[num1] ];i++)
prepare[++pre_top]=a[ table[num1] ][i];
top[ table[num1] ] = temp;
if(strcmp(c2,"onto")==0){
for(temp = top[table[num2]] ; a[ table[num2] ][ temp ] != num2 ; temp--){
target = a[ table[num2] ][ temp ];
order = top[ target ] + 1;
top[ target ]= order;
a[target][order]=target;
table[target]=target;
}
top[ table[num2] ] = temp;
}
for(order=top[ table[num2] ], i=0 ; i<=pre_top ; i++){
a[table[num2]][++order] = prepare[i];
table[prepare[i]] = table[num2];
}
top[table[num2]] = order;
}
}
for(i=0;i<amount;i++){
printf("%d:",i);
for(j=0;j<=top[i];j++)
printf(" %d",a[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
uva 100 The 3n + 1 problem
第一次寫 uva ,若有用 // 來寫 comment,需刪掉,因為用 ANSI compiler 時,不認識 //。
注意:1.input 的數字不一定是前小後大。
2.output印出的前兩個數字為 input 數字輸入的順序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int stop(int num){
int counter;
counter=1;
while(num!=1){
++counter;
if(num%2==1)
num=3*num+1;
else
num/=2;
}
return counter;
}
int main(void){
int low, high, maximum, temp_l, tmep_h;
int i, temp;
while( scanf("%d %d",&low, &high)!=EOF ){
if(low > high){
temp_l=high; tmep_h=low;
}else{
temp_l=low; tmep_h=high;
}
maximum=0;
for(i=temp_l ; i<=tmep_h ; i++){
temp = stop(i);
maximum = temp > maximum ? temp : maximum;
}
printf("%d %d %d\n", low, high, maximum);
}
return 0;
}
注意:1.input 的數字不一定是前小後大。
2.output印出的前兩個數字為 input 數字輸入的順序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int stop(int num){
int counter;
counter=1;
while(num!=1){
++counter;
if(num%2==1)
num=3*num+1;
else
num/=2;
}
return counter;
}
int main(void){
int low, high, maximum, temp_l, tmep_h;
int i, temp;
while( scanf("%d %d",&low, &high)!=EOF ){
if(low > high){
temp_l=high; tmep_h=low;
}else{
temp_l=low; tmep_h=high;
}
maximum=0;
for(i=temp_l ; i<=tmep_h ; i++){
temp = stop(i);
maximum = temp > maximum ? temp : maximum;
}
printf("%d %d %d\n", low, high, maximum);
}
return 0;
}
uva 516 Prime Land
數字都是以質因數表示。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int prime(int num){
int ok,i;
ok=1;
for(i=2;i<=sqrt(num);++i)
if(num%i==0){
ok=0;
break;
}
return ok;
}
int main(void){
double base,factor;
double number;
int div;
int counter,space;
char c,cc;
while(1){
scanf("%lf%c",&base,&c);
if(base==0)
break;
else{
scanf("%lf%c",&factor,&cc);
number = pow(base,factor);
while(1){
if(cc =='\n')
break;
scanf("%lf%c%lf%c",&base,&c,&factor,&cc);
number *= pow(base,factor);
}
}
--number;
div=number;
space=1;
while(number>1){
if(prime(div)==1){
counter=0;
while((int)number%div==0){
++counter;
number/=div;
}
if(space==1 && counter>=1){
printf("%d %d",div,counter);
space=0;
}else if(counter>=1){
printf(" %d %d",div,counter);
}
}
--div;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
int prime(int num){
int ok,i;
ok=1;
for(i=2;i<=sqrt(num);++i)
if(num%i==0){
ok=0;
break;
}
return ok;
}
int main(void){
double base,factor;
double number;
int div;
int counter,space;
char c,cc;
while(1){
scanf("%lf%c",&base,&c);
if(base==0)
break;
else{
scanf("%lf%c",&factor,&cc);
number = pow(base,factor);
while(1){
if(cc =='\n')
break;
scanf("%lf%c%lf%c",&base,&c,&factor,&cc);
number *= pow(base,factor);
}
}
--number;
div=number;
space=1;
while(number>1){
if(prime(div)==1){
counter=0;
while((int)number%div==0){
++counter;
number/=div;
}
if(space==1 && counter>=1){
printf("%d %d",div,counter);
space=0;
}else if(counter>=1){
printf(" %d %d",div,counter);
}
}
--div;
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
訂閱:
意見 (Atom)